Antimetabolites for Cancer Treatment
Antimetabolites have similar chemical structures to those of molecules the body uses to create nucleic acid (DNA and RNA). They interfere with normal cell function. Generally, antimetabolites induce cell death during the S phase of cell growth when incorporated into RNA and DNA or inhibit enzymes needed for nucleic acid production. These agents are used to treat a variety of cancers, including leukemia, breast, pancreatic, ovarian, and gastro-intestinal cancers. Antimetabolites are characterized by low molecular weights. Why can’t we just make more chemical compounds that get in the pathway? The problem for drug designers is that metabolic pathways are hard to figure out, and making compounds to interfere with them without causing other problems is fiendishly difficult. Both the pyrimidine bases (uracil, cytosine), and the purine bases (adenine, guanine) are building blocks in the synthesis of DNA and RNA nucleotides. In the replication process, nucleotides combine to form DNA strands. It is less clear how the purine antagonists function, but they may inhibit normal production of DNA.
Antimetabolite drugs were among the first effective chemotherapeutic agents discovered.
Pyrimidine Compounds
In 1957 scientists introduced 5-flurouracil (5-FU). 5-FU is a pyrimidine base containing a fluoride atom at the 5 carbon position on the ring. Uracil is a naturally occurring pyrimidine base used in nucleic acid synthesis. It is converted to thymidine by enzyme action. 5-FU is similar in structure to uracil and is converted to two active metabolites (FdUMP and FUTP) that inhibit the activity of the enzyme thymidylate synthetase. The enzyme normally converts uracil to thymidine by adding a methyl group at the fifth carbon of the pyrimidine ring. 5-FU mimics the natural base and functions to inhibit DNA synthesis. The carbon group cannot be added because of the fluoride atom at the five position. Normal DNA synthesis fails. dUTP and FdUTP are incorporated into DNA so that it cannot function normally. In addition, FUTP is incorporated into RNA leading to faulty translation of the RNA. Thus, the synthesis of multiple forms of RNA (messenger, ribosomal, transfer and small nuclear RNAs) is blocked. These combined actions on DNA and RNA are cytotoxic to the rapidly dividing cancer cells. 5-FU is used for the treatment of many malignancies: breast, head and neck, adrenal, pancreatic, gastric, colon, rectal, esophageal, liver, and G-U (bladder, penile, vulva, prostate) . 5-FU may be administered by bolus IV infusion or continuous IV infusion over two days every 2-3 weeks or by oral ingestion. In addition, it may be used to treat skin cancers (basal cell and keratosis) by topical application.
Other pyrimidine antagonists include: cytarabine, capecitabine, gemcitabine and decitabine. Cytarabine (aka arabinosylcytosine) is a deoxycytidine base compound that is converted to its active metabolite, ara-CTP. This base is incorporated into DNA and causes strand termination. The cancer cell is unable to divide. This drug has proven effective in acute non-lymphocytic, lymphocytic, myelogenous , and chronic myelocytic leukemias, as well as leptomeningeal carcinomatosis and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Capecitabine is an oral 5-FU pro-drug. It is converted to 5-FU by liver and tumor cells. It is used as adjuvant therapy in colon and breast metastasis. Gemcitabine is an ara-C prodrug which is activated by intracellular phosphorylation. This inhibits DNA and RNA synthesis. It is a first line treatment of pancreatic, metastatic breast, bladder, ovarian and non-small cell lung cancers.
Purine Compounds
There are few clinically useful purine antagonists. Scientists conjecture that these purine antagonists stop synthesis by decreasing the production of the purine bases or that the antagonist molecules themselves may be incorporated into the DNA strands during synthesis and halt cell replication. Without adequate amounts of the purine bases, nucleotide production stops and the cancer cell dies.
Fludarabine or 2-fluoro-ara-amp is an antimetabolite of the purine class. It functions as a pro-drug. It is dephosphorylated to F-ara-ATP and enters the cancer cell. Upon incorporation into the DNA strand, it halts strand lengthening. The drug has been employed to treat refractory chronic lymphocytic and chronic B cell leukemias, non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, and T- cell lymphoma.
6-Mercaptopurine (6-MP) is another purine agent used against acute lymphocytic leukemia. It is active in the S phase of cell proliferation. When it is incorporated into DNA and RNA, the nucleic acids are rendered useless. 6-MP may also act through inhibition of de novo synthesis of the purine bases. Genetic mutation may lead to purine resistance.
Adenosine deaminase inhibitors are a class of compounds that can be classified under the purine antagonist umbrella. These include Cladribine and Pentostatin.
Folate Antagonists
An early advancement in cancer research came in the mid-20th Century when pioneering researcher Sidney Farber was able to induce remission in children with leukemia using the antimetabolite drug aminopterin. In 1953 another milestone was achieved with the first cure of a solid tumor entirely with chemotherapy, the antimetabolite methotrexate. Folic acid is a necessary compound for the production of nucleotides. It was empirically observed in patients with leukemia that diets low in folate produced lower white cell counts than observed in leukemic patients on normal folate diets. In 1948, a folate antagonist was found effective in childhood leukemia. The antifolate medication methotrexate became an early chemotherapy drug. Between cells folate is converted by the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) to dihydrofolate. This compound is then reduced to tetrahydrofolate (THDF). THDF acts as a carbon carrier compound that donates methyl groups to end target molecules through the enzymatic action of thymidine synthetase. DHFR is continuously used in this process and is the site where the folate antagonists function. The drugs impede enzyme action and hence interfere with nucleotide formation.
Methotrexate binds to DHFR reversibly and inactivates it. This prevents methylation and decreases available supplies of purine and thymidine bases for new DNA and RNA synthesis. Methotrexate is active in the S phase of cell growth. It is effective in many 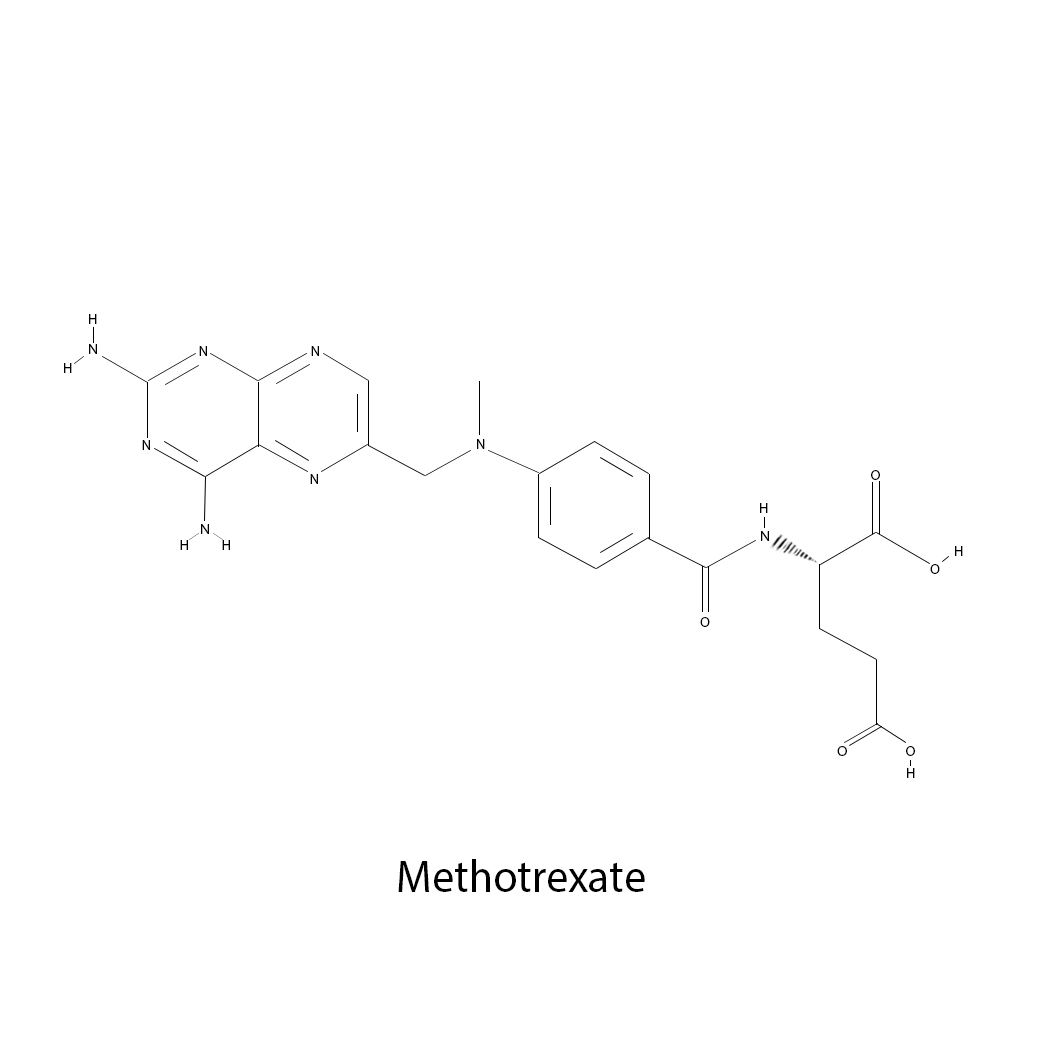 malignancies. Breast, head and neck, colorectal, non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas, osteosarcoma, bladder and choriocarcinoma are treated with methotrexate. It is also used in acute lymphocytic leukemia, and some types of meningeal carcinomas. Methotrexate is the most common folate antagonist used today even though others have been developed. Drug resistance is a primary complication of treatment with methotrexate. Decreased drug transport into the cell can occur. A lower and less effective dose of methotrexate is observed intracellulary. Genetic mutations and alterations in gene activity may occur as well which alter binding constants to the enzymes or causes increases in the DHFR enzyme within the cell.
malignancies. Breast, head and neck, colorectal, non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas, osteosarcoma, bladder and choriocarcinoma are treated with methotrexate. It is also used in acute lymphocytic leukemia, and some types of meningeal carcinomas. Methotrexate is the most common folate antagonist used today even though others have been developed. Drug resistance is a primary complication of treatment with methotrexate. Decreased drug transport into the cell can occur. A lower and less effective dose of methotrexate is observed intracellulary. Genetic mutations and alterations in gene activity may occur as well which alter binding constants to the enzymes or causes increases in the DHFR enzyme within the cell.
Pemetrexed is a folate antagonist used in the treatment of mesothelioma and non-small cell lung cancer. Pemetrexed is combined with cisplatin (an agent which promotes DNA cross-linking) to treat those cancers. Pemetrexed acts like methotrexate. It hinders multiple enzymes needed for de novo production of the thymidine and purine nucleotides. Normal DNA and RNA production is prevented. Pralatrexate is also approved for use against cancer, but it is less often used.
Demethylation Agents
Azacitidine and Decitabine work through demethylation. In normal cellular metabolism, cytosine methylation is an epigenetic mark for maintenance of gene silencing across cellular divisions. However, this chemically stable modification may be removed from DNA through demethylation. Azacitidine and Decitabine are chemical analogs of cytidine. Like other antimetabolites they can become incorporated into the nucleic acid. Once part of the cell’s DNA, it stops methylation by inhibiting DNA methyltransferase and thereby induces cell death. It may also restore normal gene function controlling cell proliferation.
Medicinal Compounds
There are 19 currently approved cancer medicines that can be classified as antimetabolites, of which 4 are antifolates.
Azacitidine (aka Azacytidine)
Brand/Trade Names: Vidazaaz
Manufacturers: Celgene, Apicore LLC, Archimica, Ash Stevens, Inc., Aspire Lifesciences Pvt Ltd
Formula: C8H12N4O5
Mechanism: demethylation. Cytidine analogue.
Class: antimetabolite, DNA methyltransferase inhibitor
Administration: Oral
Notes: Chemical analog of cytidine. An epigenetic drug. Approved by the FDA in 2004. Used for treatment of myelodysplastic syndromes and leukemia.
Capecitabine
Brand/Trade Names: Xeloda
Manufacturers: Genentech, Aarti Industries Ltd, Acebright India Pharma Private Limited, Apotex Pharmachem, Archimica
Formula: C15H22FN3O6
Mechanism: antimetabolite
Class: Pyrimidine analogue
Administration: Oral
Notes: Approved by the FDA in 2005. Used for treatment of breast cancer and colorectal cancer.
Clofarabine
Brand/Trade Names: Clolar
Manufacturers: Sanofi-Aventis US LLC Apicore LLC Biophore India Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd Emcure Pharmaceuticals Hangzhou Longshine Bio-Tech Co., Ltd
Formula: C10H11ClFN5O3
Mechanism: antimetabolite
Class: Purine analogue
Administration: Intravenous
Notes: Approved by the FDA in 2004. Used for treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Cladribine
Brand/Trade Names: Leustatin, Litak
Manufacturers: Reliable Biopharmaceutical Corporation, Ahk Tech, Aspen Biopharma Labs Pvt Ltd, Biophore India Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd, Cilag AG
Formula: C10H12ClN5O3
Mechanism: antimetabolite, adenosine deaminase inhibitor
Class: Purine analogue
Administration: Oral
Notes: Approved by the FDA in 1993. Used for treatment of hairy cell leukemia, acute myeloid leukemia, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and lymphoma.
Cytarabine
Brand/Trade Names: Cytosar-U, Arabinosylcytosine
Manufacturers: Pharmacia & Upjohn Company LLC, Ahk Tech, Apotex Pharmachem Inc., Archimica, Asahi Kasei Finechem
Formula: C9H13N3O5
Mechanism: antimetabolite
Class: Cytosine analogue
Administration: Intravenous
Notes: Approved by the FDA in 1992. Used for treatment of leukemia.
Decitabine
Brand/Trade Names: Dacogen
Manufacturers: Otsuka America Pharmaceuticals, Fujifilm Diosynth Biotechnologies
Formula: C8H12N4O4
Mechanism: antimetabolite, demethylation
Class: Cytosine analogue, DNA methyltransferase inhibitor
Administration: Intravenous
Notes: Cytidine analog. An epigenetic drug. Approved by the FDA in 2006. Used for myelodysplastic syndromes.
Fludarabine
Brand/Trade Names: Fludara
Manufacturers: Actavis Pharma Inc, Archimica, Ash Stevens, Inc., Aspen Biopharma Labs Pvt Ltd, Beijing Lunarsun Pharmaceutical Co.
Formula: C10H13FN5O7P
Mechanism: antimetabolite
Class: Purine analogue
Administration: Intravenous
Notes: purine analog. Approved by the FDA in 1991. Used for chronic lymphocytic leukemia, lymphoma.
Fluorouracil (5F0U)
Brand/Trade Names: Abdrucil, 5-FU
Manufacturers: Teva Parenteral Medicines, AMCOL Health and Beauty Solutions, Biotechnica Pharma Global, DCS Pharma AG, DSM Nutritional Products
Formula: C4H3FN2O2
Mechanism: antimetabolite
Class: Pyrimidine analogue
Administration: Intravenous
Notes: Approved by the FDA in 1962. Used for treatment of bladder, anal, breast, gastrointestinal, thymic, cervical, head and neck, and colorectal cancer
Floxuridine
Brand/Trade Names: FUDR
Manufacturers: Zhejiang Hisun Pharmaceutical, ORGANICA Feinchemie GmbH Wolfen, Reliable Biopharmaceutical Corporation
Formula: C9H11FN2O5
Mechanism: antimetabolite
Class: Pyrimidine analogue
Administration: Intravenous
Notes: Chemical analog of pyrimidine. First approved by the FDA in 1970. Used for stomach, colon, and kidney cancer.
Gemcitabine
Brand/Trade Names: Gemzar
Manufacturers: Evonik Corporation, Arch Pharmalabs, Archimica, Arene Lifesciences Limited, Aspen Biopharma Labs Pvt Ltd
Formula: C9H11F2N3O4
Mechanism: antimetabolite
Class: Pyrimidine analogue
Administration: Intravenous
Notes: Approved by the FDA in 1996. Approved for treatment of sarcoma, pancreatic cancer, ovarian cancer, breast cancer, and non-small cell lung cancer.
Hydroxyurea
Brand/Trade Names: Hydroxycarbamide, Hydrea, Droxia, Mylocel
Manufacturers: Qilu Pharmaceutical Co., Archimica, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Nishchem International Pvt., Olon Spa
Formula: CH4N2O2
Mechanism: antimetabolite
Class:
Administration: Intravenous
Notes: Approved by the FDA in 1967. Used for treatment of chronic myelogenous leukemia, squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck, melanoma, and ovarian cancer.
Mercaptopurine
Brand/Trade Names: Purinethol, Purixan
Manufacturers: Aarti Industries Ltd, Ajinomoto Company, Changzhou Siyao Pharmaceuticals Co., Fermion Oy, Stason Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Formula: C5H4N4S
Mechanism: antimetabolite
Class: Purine analogue
Administration: Oral
Notes: Approved by the FDA in 1953. Used for treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Nelarabine
Brand/Trade Names: Arranon
Manufacturers: Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, ALP Pharm Beijing Co., Biophore India Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd, ChemWerth Inc, F.I.S. Fabbrica Italiana Sintetici SpA
Formula: C11H15N5O5
Mechanism: antimetabolite
Class: Purine analogue
Administration: Intravenous
Notes: Approved by the FDA in 2005. Used for treatment of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia and T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma.
Pentostatin
Brand/Trade Names: Nipent
Manufacturers: Hospira, Inc Apicore LLC Biotechnica Pharma Global ChemPacific Corp
Formula: C11H16N4O4
Mechanism: antimetabolite, adenosine deaminase inhibitor
Class: Purine analogue
Administration: Intravenous
Notes: Approved by the FDA in 1991. Used for hairy cell leukemia.
Thioguanine
Brand/Trade Names: Tabloid
Manufacturers: Glaxo Operations UK Limited t/a Glaxo Welcome Operations
Formula: C5H5N5S
Mechanism: antimetabolite
Class: Purine analogue
Administration: Oral
Notes: Approved by the FDA in 1966. Used for treatment of acute myeloid leukemia.
Trifluridine/Tipiricil
Brand/Trade Names: Lonsurf
Manufacturers: Taiho Pharmaceuticals Co Ltd
Formula: C5H5N5S
Mechanism: antimetabolite
Class: Pyrimidine analogue
Administration: Oral
Notes: Approved by the FDA in 2015. Used to treat colorectal cancer and stomach adenocarcinoma.
Antifolates
Pralatrexate
Brand/Trade Names: Folotyn
Manufacturers: Allos Therapeutics, Epoch Labs, Haoyuan Chemexpress Co., Hetero Drugs Limited. Mac-Chem Products (India) Pvt.
Formula: C23H23N7O5
Mechanism: antimetabolite
Class: Antifolate Administration: Intravenous Notes: Approved by the FDA in 2009. Used for treatment of lymphoma.
Pemetrexed
Brand/Trade Names: Alimta
Manufacturers: Eli Lilly and Company, Acebright India Pharma Private Limited. Arene Lifesciences Limited, Aspire Lifesciences Pvt Ltd, BrightGene Bio-Medical Technology Co.
Formula: C20H21N5O6
Mechanism: antimetabolite
Class: Antifolate
Administration: Intravenous Notes: Approved by the FDA in 2004. Used for treatment of mesothelioma and non-small cell lung cancer.
Methotrexate
Brand/Trade Names: MTX, amethopterin
Manufacturers: Bedford Labs, Biesterfeld Spezialchemie GmbH, Biovectra Inc, CF Pharma Ltd., Excella GmbH
Formula: C20H22N8O5
Mechanism: antimetabolite
Class: Antifolate
Administration: Intravenous
Notes: Approved by the FDA in 1953. Used by breast cancer, osteosarcoma, leukemia, lung cancer, lymphoma, head and neck cancer, and stomach cancer.  PDF list of antimetabolites.
PDF list of antimetabolites.